The osquery tooling needed a little work to be fully automated and repeatable. This change tunes up the tools and makes the entire deployment process multi-node capable and repeatable. The osquery role was vendored because of bugs within their use of aarmor profiles and there was no way to disable them. The fleet use of commands for ssl creation have been removed. The ssl modules are now being used to generate all of the certificates. New pre-tasks have been added to check for required variables. If the required variables are not set the playbooks will fail early and notify the user of the issue. Change-Id: I88c2b40ed9d9a88a39bdf07b0dce2900fda50151 Signed-off-by: Kevin Carter <kevin.carter@rackspace.com> |
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| assets | ||
| conf.d | ||
| env.d | ||
| roles | ||
| vars | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| ansible-role-requirements.yml | ||
| bootstrap-embedded-ansible.sh | ||
| haproxy.example | ||
| installDB.yml | ||
| installKolideFleet.yml | ||
| installOSquery.yml | ||
| inventory.example.yml | ||
| README.rst | ||
| site-fleet.yml | ||
| site-osquery.yml | ||
| site.yml | ||
Install OSQuery and Kolide fleet
- tags
-
openstack, ansible
Table of Contents
- [About this repository](#about-this-repository)
- [OpenStack-Ansible Integration](#openstack-ansible-integration)
- [TODO](#todo)
About this repository
This set of playbooks will deploy osquery. If this is being deployed as part of an OpenStack all of the inventory needs will be provided for.
These playbooks require Ansible 2.4+.
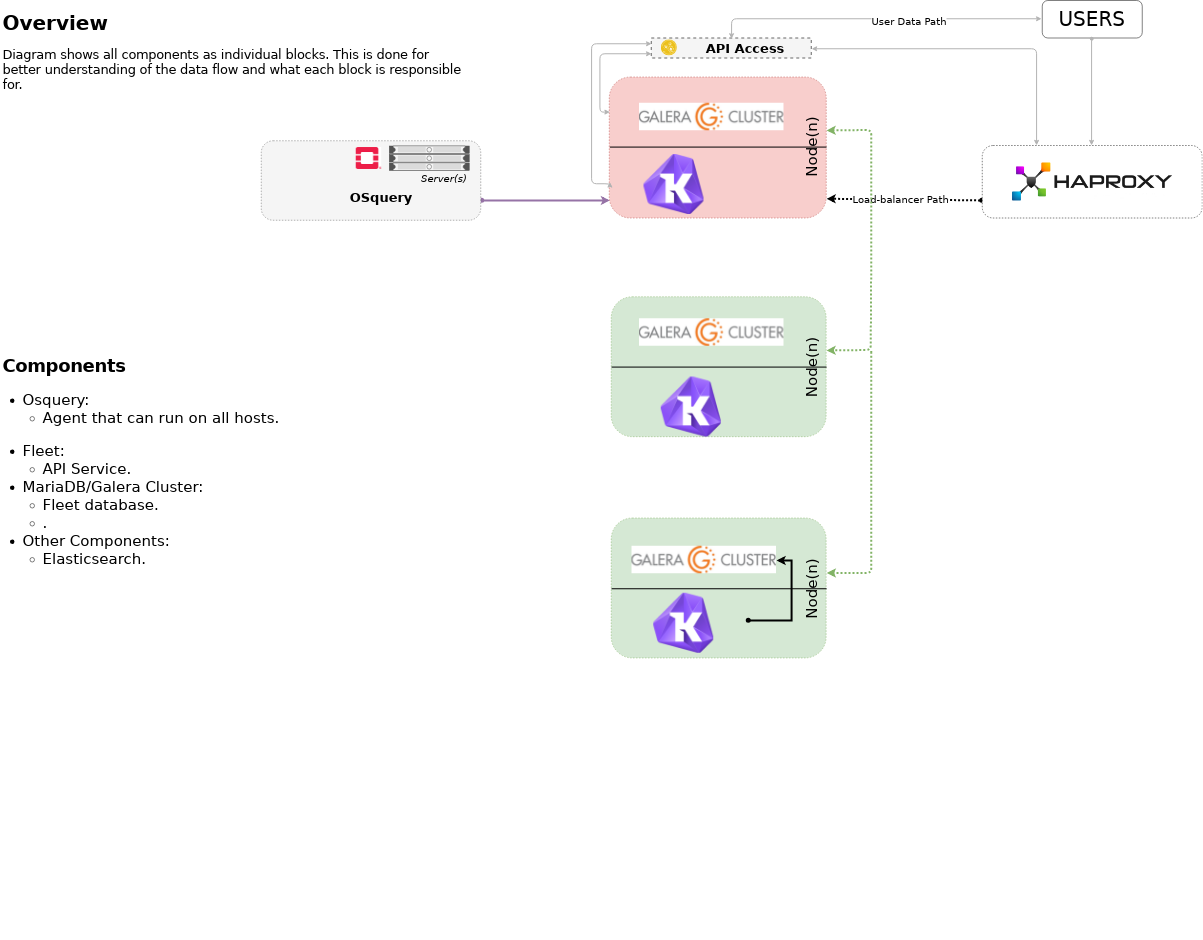
Highlevel overview of Osquery & Kolide Fleet infrastructure these playbooks will build and operate against.
OpenStack-Ansible Integration
These playbooks can be used as standalone inventory or as an
integrated part of an OpenStack-Ansible deployment. For a simple example
of standalone inventory, see inventory.example.yml.
Setup | system configuration
Clone the osquery-osa repo
cd /opt
git clone https://github.com/openstack/openstack-ansible-opsCopy the env.d file into place
cd /opt/openstack-ansible-ops/osquery
cp env.d/fleet.yml /etc/openstack_deploy/env.d/Copy the conf.d file into place
cp conf.d/fleet.yml /etc/openstack_deploy/conf.d/In fleet.yml, list your logging hosts under fleet-logstash_hosts to create the kolide fleet cluster in multiple containers and one logging host under fleet_hosts to create the fleet container
vi /etc/openstack_deploy/conf.d/fleet.ymlCreate the containers
cd /opt/openstack-ansible/playbooks
openstack-ansible lxc-containers-create.yml --limit fleet_allUpdate the /etc/hosts file (optional)
cd /opt/openstack-ansible/playbooks
openstack-ansible openstack-hosts-setup.ymlCreate an haproxy entry for kolide-fleet service 8443
cd /opt/openstack-ansible-ops/osquery
cat haproxy.example >> /etc/openstack_deploy/user_variables.yml
cd /opt/openstack-ansible/playbooks/
openstack-ansible haproxy-install.yml --tags=haproxy-service-configDeploying | Installing with embedded Ansible
If this is being executed on a system that already has Ansible installed but is incompatible with these playbooks the script bootstrap-embedded-ansible.sh can be sourced to grab an embedded version of Ansible prior to executing the playbooks.
source bootstrap-embedded-ansible.shDeploying | Manually resolving the dependencies
This playbook has external role dependencies. If Ansible is not
installed with the bootstrap-ansible.sh
script these dependencies can be resolved with the
ansible-galaxy command and the
ansible-role-requirements.yml file.
- Example galaxy execution
ansible-galaxy install -r ansible-role-requirements.yml --roles-path=~/ansible25/repositories/rolesIn the even that some of the modules are alread installed execute the following
ansible-galaxy install -r ansible-role-requirements.yml --ignore-errors --roles-path=~/ansible25/repositories/rolesOnce the dependencies are set make sure to set the action plugin path to the location of the config_template action directory. This can be done using the environment variable ANSIBLE_ACTION_PLUGINS or through the use of an ansible.cfg file.
Deploying | The environment
Create some basic passwords keys that are needed by fleet .. code-block:: bashG
echo "kolide_fleet_db_password: $(openssl rand -base64 16)" > /etc/openstack_deploy/fleet_user_vars.yml echo "kolide_fleet_jwt_key: $(openssl rand -base64 32)" >> /etc/openstack_deploy/fleet_user_vars.yml echo "kolide_fleet_admin_password: $(openssl rand -base64 16)" >> /etc/openstack_deploy/fleet_user_vars.yml echo "mariadb_root_password: $(openssl rand -base64 16)" >> /etc/openstack_deploy/fleet_user_vars.yml
Install master/data Fleet nodes on the elastic-logstash containers, deploy logstash, deploy Kibana, and then deploy all of the service beats.
cd /opt/openstack-ansible-ops/osquery
ansible-playbook site.yml -e@/etc/openstack_deploy/fleet_user_vars.yml- The openstack-ansible command can be used if the version of ansible on the system is greater than 2.5. This will automatically pick up the necessary group_vars for hosts in an OSA deployment.
- If required add
-e@/opt/openstack-ansible/inventory/group_vars/all/all.ymlto import sufficient OSA group variables to define the OpenStack release. Journalbeat will then deploy onto all hosts/containers for releases prior to Rocky, and hosts only for Rocky onwards. If the variableopenstack_releaseis undefined the default behaviour is to deploy Journalbeat to hosts only. - Alternatively if using the embedded ansible, create a symlink to include all of the OSA group_vars. These are not available by default with the embedded ansible and can be symlinked into the ops repo.
ln -s /opt/openstack-ansible/inventory/group_vars /opt/openstack-ansible-ops/osquery/group_varsThe individual playbooks found within this repository can be independently run at anytime.
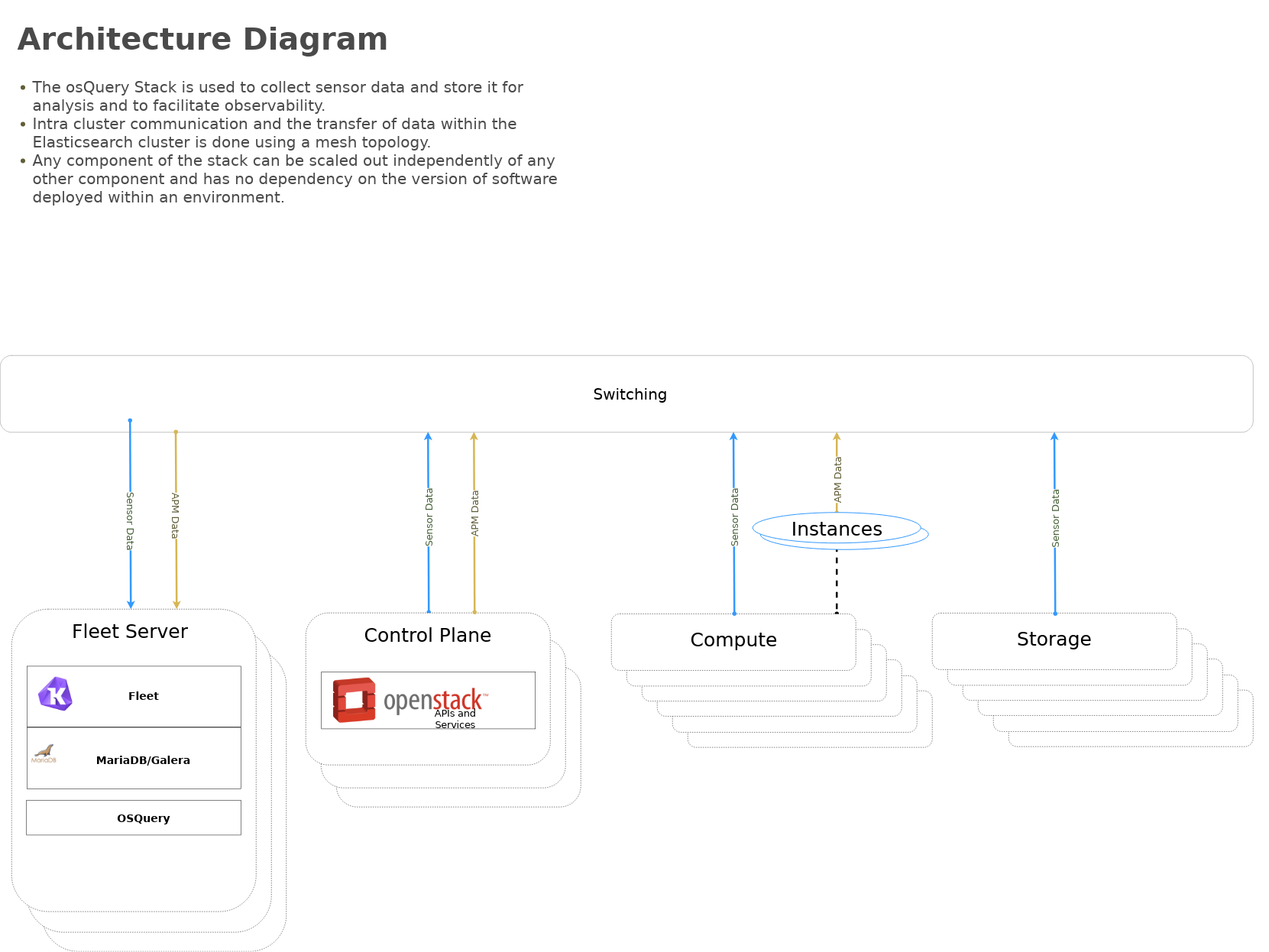
Architecture | Data flow
This diagram outlines the data flow from within an Elastic-Stack deployment.
TODO
- The following is a list of open items.
-
- [x] Test Redhat familly Operating Systems
- [x] missing mariadb cluster (should all work needs additional vars)
- [ ] use haproxy instead of the kolide fleet server ip
- [ ] add/update tags
- [ ] convert to roles
- [ ] add testing