|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| assets | ||
| doc/source | ||
| playbooks | ||
| roles | ||
| galaxy.yml | ||
| README.rst | ||
Install vexxhost magnum-cluster-api driver
About this repository
This repository includes playbooks and roles to deploy the Vexxhost magnum-cluster-api driver for the OpenStack Magnum service.
The playbooks create a complete deployment including the control plane k8s cluster which should result in a ready-to-go experience for operators.
The following architectural features are present:
- The control plane k8s cluster is an integral part of the openstack-ansible deployment, and forms part of the foundational components alongside mariadb and rabbitmq.
- The control plane k8s cluster is deployed on the infra hosts and integrated with the haproxy loadbalancer and OpenStack internal API endpoint, and not exposed outside of the deployment
- SSL is supported between all components and configuration is possible to support different certificate authorities on the internal and external loadbalancer endpoints.
- Control plane traffic can stay entirely within the management network if required
- The magnum-cluster-api-proxy service is deployed to allow communication between the control plane and workload clusters when a floating IP is not attached to the workload cluster.
- It is possible to do a completely offline install for airgapped environments
The magnum-cluster-api driver for magnum can be found here https://github.com/vexxhost/magnum-cluster-api
Documentation for the Vexxhost magnum-cluster-api driver is here https://vexxhost.github.io/magnum-cluster-api/
The ansible collection used to deploy the controlplane k8s cluster is here https://github.com/vexxhost/ansible-collection-kubernetes
The ansible collection used to deploy the container runtime for the controlplane k8s cluster is here https://github.com/vexxhost/ansible-collection-containers
These playbooks require Openstack-Ansible Caracal or later.
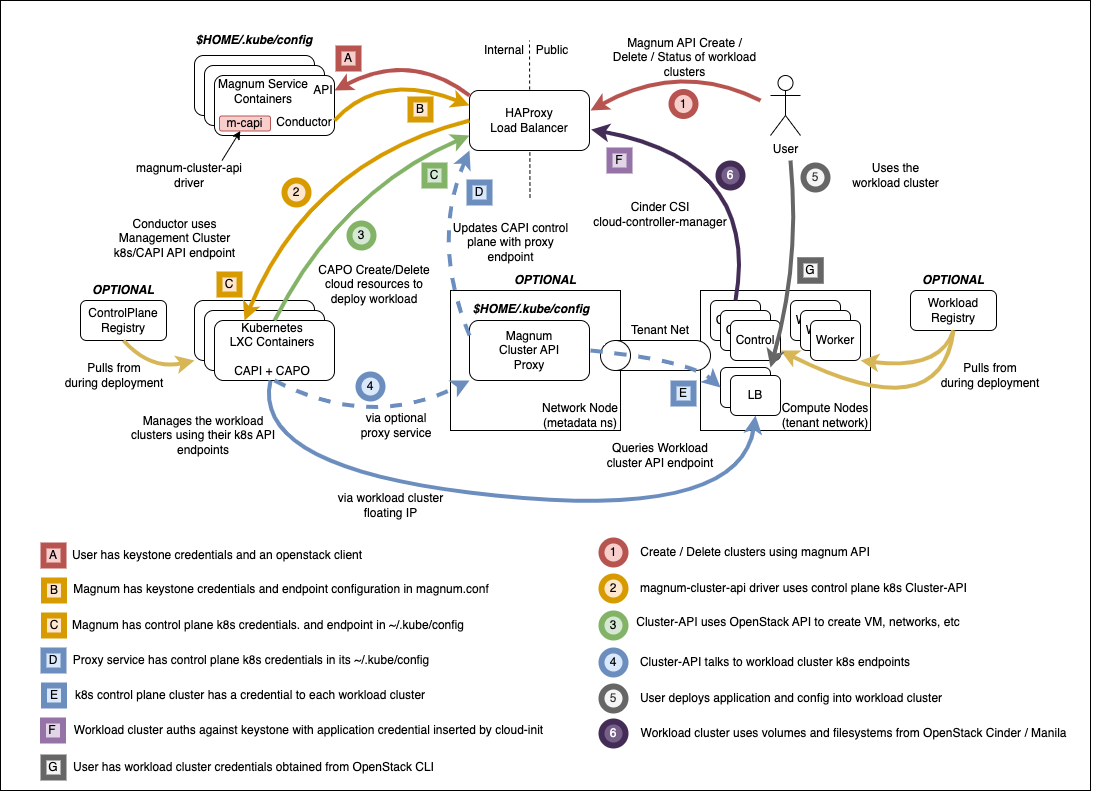
Highlevel overview of the Magnum infrastructure these playbooks will build and operate against.
Pre-requisites
- An existing openstack-ansible deployment
- Control plane using LXC containers, bare metal deployment is not tested
- Core openstack services plus Octavia
OpenStack-Ansible Integration
The playbooks are distributed as an ansible collection, and integrate with Openstack-Ansible by adding the collection to the deployment host by adding the following to /etc/openstack_deploy/user-collection-requirements.yml under the collections key.
collections: - name: vexxhost.kubernetes source: https://github.com/vexxhost/ansible-collection-kubernetes type: git version: main - name: osa_ops.mcapi_vexxhost type: git version: master source: https://opendev.org/openstack/openstack-ansible-ops#/mcapi_vexxhost
The collections can then be installed with the following command:
cd /opt/openstack-ansible openstack-ansible scripts/get-ansible-collection-requirements.yml
The modules in the kubernetes collection require an additional python module to be present in the ansible-runtime python virtual environment. Specify this in /etc/openstack_deploy/user-ansible-venv-requirements.txt
docker-image-py
OpenStack-Ansible configuration for magnum-cluster-api driver
Specify the deployment of the control plane k8s cluster in /etc/openstack_deploy/env.d/k8s.yml
--- component_skel: k8s_capi: belongs_to: - k8s_all container_skel: k8s_container: belongs_to: - cluster-api_containers contains: - k8s_capi physical_skel: cluster-api_containers: belongs_to: - all_containers cluster-api_hosts: belongs_to: - hosts
Define the physical hosts that will host the controlplane k8s cluster, this example is for an all-in-one deployment and should be adjusted to match a real deployment with multiple hosts if high availability is required.
cluster-api_hosts: aio1: ip: 172.29.236.100
Integrate the control plane k8s cluster with the haproxy loadbalancer in /etc/openstack-deploy/group_vars/k8s_all/haproxy_service.yml
--- haproxy_k8s_service: haproxy_service_name: k8s haproxy_backend_nodes: "{{ groups['k8s_all'] | default([]) }}" haproxy_ssl: false haproxy_ssl_all_vips: false haproxy_port: 6443 haproxy_balance_type: tcp haproxy_balance_alg: leastconn haproxy_interval: '15000' haproxy_backend_port: 6443 haproxy_backend_rise: 2 haproxy_backend_fall: 2 haproxy_timeout_server: '15m' haproxy_timeout_client: '5m' haproxy_backend_options: - tcplog - ssl-hello-chk - log-health-checks haproxy_backend_httpcheck_options: - 'send hdr User-Agent "osa-haproxy-healthcheck" meth GET uri /healthz' haproxy_backend_server_options: - check-ssl - verify none haproxy_accept_both_protocols: "{{ k8s_accept_both_protocols | default(openstack_service_accept_both_protocols) }}" haproxy_service_enabled: "{{ groups['k8s_all'] is defined and groups['k8s_all'] | length > 0 }}" k8s_haproxy_services: - "{{ haproxy_k8s_service | combine(haproxy_k8s_service_overrides | default({})) }}"
Configure the LXC container that will host the control plane k8s cluster to be suitable for running nested containers in /etc/openstack-deploy/group_vars/k8s_all/main.yml
--- lxc_container_config_list: - "lxc.apparmor.profile=unconfined" lxc_container_mount_auto: - "proc:rw" - "sys:rw"
Set up config-overrides for the magnum service in /etc/openstack-deploy/user_variables_magnum.yml. Adjust the images and flavors here as necessary, these are just for demonstration. Upload as many images as you need for the different workload cluster kubernetes versions.
#list the images to upload to glance here, or set to an empty list #to handle image uploading by some other means magnum_glance_images: - disk_format: qcow2 distro: ubuntu file: https://object-storage.public.mtl1.vexxhost.net/swift/v1/a91f106f55e64246babde7402c21b87a/magnum-capi/ubuntu-2204-kube-v1.23.17.qcow2 image_format: bare name: ubuntu-2204-kube-v1.23.17 public: true #the cluster templates cannot be created during the magnum installation #as the control plane k8s credentials must be in place first magnum_cluster_templates: [] #any flavors specified in the cluster template must already exist #the magnum playbook can create flavors, or set to an empty list #to handle flavor creation by some other means magnum_flavors: - cloud: default disk: 40 name: m1.medium ram: 4096 vcpus: 2Set up config-overrides for the control plane k8s cluster in /etc/openstack-deploy/user_variables_k8s.yml` Attention must be given to the SSL configuration. Users and workload clusters will interact with the external endpoint and must trust the SSL certificate. The magnum service and cluster-api can be configured to interact with either the external or internal endpoint and must trust the SSL certificiate. Depending on the environment, these may be derived from different certificate authorities.
# connect ansible group, host and network addresses into control plane k8s deployment kubernetes_control_plane_group: k8s_all kubelet_hostname: "{{ ansible_facts['hostname'] }}" kubelet_node_ip: "{{ management_address }}" kubernetes_hostname: "{{ internal_lb_vip_address }}" kubernetes_non_init_namespace: true # install the vexxhost magnum-cluster-api plugin into the magnum venv magnum_user_pip_packages: - git+https://github.com/vexxhost/magnum-cluster-api@main#egg=magnum-cluster-api # make the required settings in magnum.conf magnum_config_overrides: drivers: # ensure that the external VIP CA is trusted by the workload cluster openstack_ca_file: '/usr/local/share/ca-certificates/ExampleCorpRoot.crt' capi_client: # ensure that the internal VIP CA is trusted by the CAPI driver ca_file: '/usr/local/share/ca-certificates/ExampleCorpRoot.crt' endpoint: 'internalURL' cluster_template: # the only permitted workload network driver is calico kubernetes_allowed_network_drivers: 'calico' kubernetes_default_network_driver: 'calico' certificates: # store certificates in the magnum database instead of barbican cert_manager_type: x509keypair # Pick a range of addresses for the control plane k8s cluster cilium # network that do not collide with anything else in the deployment cilium_ipv4_cidr: 172.29.200.0/22 # Set this manually, or kube-proxy will try to do this - not possible # in a non-init namespace and will fail in LXC openstack_host_nf_conntrack_max: 1572864 # OSA containers do not run ssh so cannot use the ansible synchronize module upload_helm_chart_method: copy
Run the deployment
For a new deployment
Run the OSA playbooks/setup.yml playbooks as usual, following the normal deployment guide.
Run the magnum-cluster-api deployment
openstack-ansible osa_ops.mcapi_vexxhost.k8s_install
For an existing deployment
Ensure that the python modules required for ansible are present:
./scripts/bootstrap-ansible.sh
Alternatively, without re-running the bootstrap script:
/opt/ansible-runtime/bin/pip install docker-image-py
Add the magnum-cluser-api driver to the magnum service
openstack-ansible playbooks/os-magnum-install.yml
Create the k8s control plane containers
openstack-ansible playbooks/lxc-containers-create.yml --limit k8s_all
Run the magnum-cluster-api deployment
openstack-ansible osa_ops.mcapi_vexxhost.k8s_install
Optionally run a functional test of magnum-cluster-api
This can be done quickly using the following playbook
openstack-ansible osa_ops.mcapi_vexxhost.functional_test
This playbook will create a neutron public network, download a prebuilt k8s glance image, create a nova flavor and a magnum cluster template.
It will then deploy the workload k8s cluster using magnum, and run a sonobouy "quick mode" test of the workload cluster.
This playbook is intended to be used on an openstack-ansible all-in-one deployment.
Use Magnum to create a workload cluster
Upload Images
Create a cluster template
Create a workload cluster
Optional Components
Deploy the workload clusters with a local registry
TODO - describe how to do this
Deploy the control plane cluster from a local registry
TODO - describe how to do this
Use of magnum-cluster-api-proxy
TODO - describe what this is for
Troubleshooting
Local testing
An OpenStack-Ansible all-in-one configured with Magnum and Octavia is capable of running a functioning magnum-cluster-api deployment.
Sufficient memory should be available beyond the minimum 8G usually required for an all-in-one. A multinode workload cluster may require nova to boot several Ubuntu images in addition to an Octavia loadbalancer instance. 64G would be an appropriate amount of system RAM.
There also must be sufficient disk space in /var/lib/nova/instances to support the required number of instances - the normal minimum of 60G required for an all-in-one deployment will be insufficient, 500G would be plenty.