Change-Id: Ic9caa6b15da7bc4e91d6f5c60b74df02bfbecbd7 Implements: blueprint installguide-liberty
18 KiB
Install and configure network node
The network node primarily handles internal and external routing and
DHCP services for
virtual networks.
To configure prerequisites
Before you install and configure OpenStack Networking, you must configure certain kernel networking parameters.
Edit the
/etc/sysctl.conffile to contain the following parameters:net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter=0 net.ipv4.conf.default.rp_filter=0Implement the changes:
# sysctl -p
rdo or ubuntu or obs
To install the Networking components
ubuntu
# apt-get install neutron-plugin-ml2 neutron-plugin-openvswitch-agent \
neutron-l3-agent neutron-dhcp-agent neutron-metadata-agentrdo
# yum install openstack-neutron openstack-neutron-ml2 openstack-neutron-openvswitchobs
# zypper install --no-recommends openstack-neutron-openvswitch-agent \
openstack-neutron-l3-agent \
openstack-neutron-dhcp-agent openstack-neutron-metadata-agent ipsetNote
SUSE does not use a separate ML2 plug-in package.
debian
To install and configure the Networking components
# apt-get install neutron-plugin-openvswitch-agent openvswitch-datapath-dkms \ neutron-l3-agent neutron-dhcp-agent neutron-metadata-agentNote
Debian does not use a separate ML2 plug-in package.
Respond to prompts for database management, Identity service credentials, service endpoint registration, and message queue credentials.
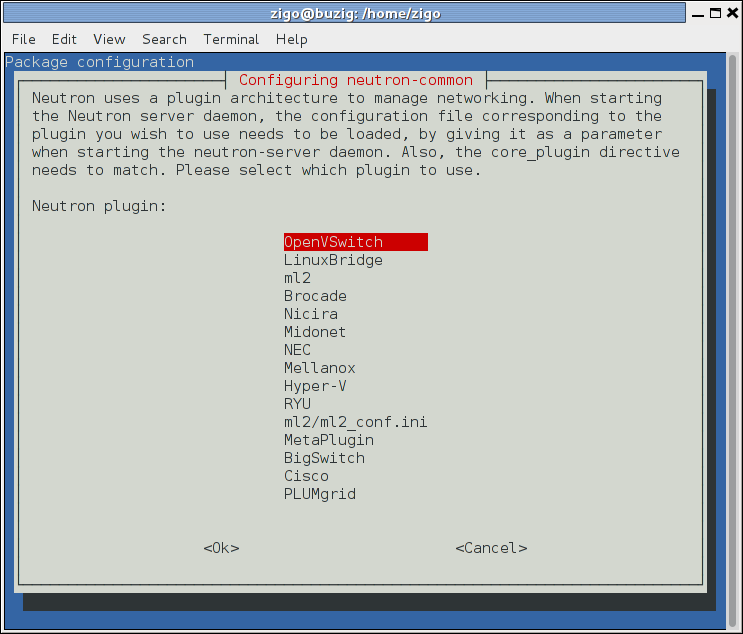
Select the ML2 plug-in:
Note
Selecting the ML2 plug-in also populates the
service_pluginsandallow_overlapping_ipsoptions in the/etc/neutron/neutron.conffile with the appropriate values.
rdo or ubuntu or obs
To configure the Networking common components
The Networking common component configuration includes the authentication mechanism, message queue, and plug-in.
Note
Default configuration files vary by distribution. You might need to add these sections and options rather than modifying existing sections and options. Also, an ellipsis (...) in the configuration snippets indicates potential default configuration options that you should retain.
Open the
/etc/neutron/neutron.conffile and edit the[database]section. Comment out anyconnectionoptions because network nodes do not directly access the database.In the
[DEFAULT]and[oslo_messaging_rabbit]sections, configure RabbitMQ message queue access:[DEFAULT] ... rpc_backend = rabbit [oslo_messaging_rabbit] ... rabbit_host = controller rabbit_userid = openstack rabbit_password = RABBIT_PASSReplace
RABBIT_PASSwith the password you chose for theopenstackaccount in RabbitMQ.In the
[DEFAULT]and[keystone_authtoken]sections, configure Identity service access:[DEFAULT] ... auth_strategy = keystone [keystone_authtoken] ... auth_uri = http://controller:5000 auth_url = http://controller:35357 auth_plugin = password project_domain_id = default user_domain_id = default project_name = service username = neutron password = NEUTRON_PASSReplace
NEUTRON_PASSwith the password you chose or theneutronuser in the Identity service.Note
Comment out or remove any other options in the
[keystone_authtoken]section.In the
[DEFAULT]section, enable the Modular Layer 2 (ML2) plug-in, router service, and overlapping IP addresses:[DEFAULT] ... core_plugin = ml2 service_plugins = router allow_overlapping_ips = True(Optional) To assist with troubleshooting, enable verbose logging in the
[DEFAULT]section:[DEFAULT] ... verbose = True
To configure the Modular Layer 2 (ML2) plug-in
The ML2 plug-in uses the Open vSwitch (OVS) <Open vSwitch> mechanism
(agent) to build the virtual networking framework for instances.
Open the
/etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/ml2_conf.inifile and edit the[ml2]section. Enable theflat <flat network>,VLAN <VLAN network>,generic routing encapsulation (GRE), andvirtual extensible LAN (VXLAN)network type drivers, GRE tenant networks, and the OVS mechanism driver:[ml2] ... type_drivers = flat,vlan,gre,vxlan tenant_network_types = gre mechanism_drivers = openvswitchIn the
[ml2_type_flat]section, configure the external flat provider network:[ml2_type_flat] ... flat_networks = externalIn the
[ml2_type_gre]section, configure the tunnel identifier (id) range:[ml2_type_gre] ... tunnel_id_ranges = 1:1000In the
[securitygroup]section, enable security groups, enableipset, and configure the OVSiptablesfirewall driver:[securitygroup] ... enable_security_group = True enable_ipset = True firewall_driver = neutron.agent.linux.iptables_firewall.OVSHybridIptablesFirewallDriverIn the
[ovs]section, enable tunnels, configure the local tunnel endpoint, and map the external flat provider network to thebr-exexternal network bridge:[ovs] ... local_ip = INSTANCE_TUNNELS_INTERFACE_IP_ADDRESS bridge_mappings = external:br-exReplace
INSTANCE_TUNNELS_INTERFACE_IP_ADDRESSwith the IP address of the instance tunnels network interface on your network node.In the
[agent]section, enable GRE tunnels:[agent] ... tunnel_types = gre
To configure the Layer-3 (L3) agent
The Layer-3 (L3) agent provides routing services for
virtual networks.
Open the
/etc/neutron/l3_agent.inifile edit the[DEFAULT]section. Configure the interface driver, external network bridge, and enable deletion of defunct router namespaces:[DEFAULT] ... interface_driver = neutron.agent.linux.interface.OVSInterfaceDriver external_network_bridge = router_delete_namespaces = TrueThe
external_network_bridgeoption intentionally lacks a value to enable multiple external networks on a single agent.(Optional) To assist with troubleshooting, enable verbose logging in the
[DEFAULT]section:[DEFAULT] ... verbose = True
To configure the DHCP agent
The DHCP agent
provides DHCP services for virtual networks.
Open the
/etc/neutron/dhcp_agent.inifile and edit the[DEFAULT]section, configure the interface and DHCP drivers and enable deletion of defunct DHCP namespaces:[DEFAULT] ... interface_driver = neutron.agent.linux.interface.OVSInterfaceDriver dhcp_driver = neutron.agent.linux.dhcp.Dnsmasq dhcp_delete_namespaces = True(Optional) To assist with troubleshooting, enable verbose logging in the
[DEFAULT]section:[DEFAULT] ... verbose = True(Optional) Tunneling protocols such as GRE include additional packet headers that increase overhead and decrease space available for the payload or user data. Without knowledge of the virtual network infrastructure, instances attempt to send packets using the default Ethernet
maximum transmission unit (MTU)of 1500 bytes.Internet protocol (IP)networks contain thepath MTU discovery (PMTUD)mechanism to detect end-to-end MTU and adjust packet size accordingly. However, some operating systems and networks block or otherwise lack support for PMTUD causing performance degradation or connectivity failure.Ideally, you can prevent these problems by enabling
jumbo frames <jumbo frame>on the physical network that contains your tenant virtual networks. Jumbo frames support MTUs up to approximately 9000 bytes which negates the impact of GRE overhead on virtual networks. However, many network devices lack support for jumbo frames and OpenStack administrators often lack control over network infrastructure. Given the latter complications, you can also prevent MTU problems by reducing the instance MTU to account for GRE overhead. Determining the proper MTU value often takes experimentation, but 1454 bytes works in most environments. You can configure the DHCP server that assigns IP addresses to your instances to also adjust the MTU.Note
Some cloud images ignore the DHCP MTU option in which case you should configure it using metadata, a script, or another suitable method.
Open the
/etc/neutron/dhcp_agent.inifile and edit the[DEFAULT]section. Enable thednsmasqconfiguration file:[DEFAULT] ... dnsmasq_config_file = /etc/neutron/dnsmasq-neutron.confCreate and edit the
/etc/neutron/dnsmasq-neutron.conffile to enable the DHCP MTU option (26) and configure it to 1454 bytes:dhcp-option-force=26,1454Kill any existing dnsmasq processes:
# pkill dnsmasq
To configure the metadata agent
The metadata agent <Metadata agent> provides
configuration information such as credentials to instances.
Open the
/etc/neutron/metadata_agent.inifile and edit the[DEFAULT]section, configure access parameters:[DEFAULT] ... auth_uri = http://controller:5000 auth_url = http://controller:35357 auth_region = RegionOne auth_plugin = password project_domain_id = default user_domain_id = default project_name = service username = neutron password = NEUTRON_PASSReplace
NEUTRON_PASSwith the password you chose for theneutronuser in the Identity service.In the
[DEFAULT]section, configure the metadata host:[DEFAULT] ... nova_metadata_ip = controllerIn the
[DEFAULT]section, configure the metadata proxy shared secret:[DEFAULT] ... metadata_proxy_shared_secret = METADATA_SECRETReplace
METADATA_SECRETwith a suitable secret for the metadata proxy.(Optional) To assist with troubleshooting, enable verbose logging in the
[DEFAULT]section:[DEFAULT] ... verbose = TrueOn the controller node, open the
/etc/nova/nova.conffile and edit the[neutron]section to enable the metadata proxy and configure the secret:[neutron] ... service_metadata_proxy = True metadata_proxy_shared_secret = METADATA_SECRETReplace
METADATA_SECRETwith the secret you chose for the metadata proxy.On the controller node, restart the Compute
APIservice:rdo or obs
# systemctl restart openstack-nova-api.serviceubuntu or debian
# service nova-api restart
To configure the Open vSwitch (OVS) service
The OVS service provides the underlying virtual networking framework
for instances. The integration bridge br-int handles
internal instance network traffic within OVS. The external bridge
br-ex handles external instance network traffic within OVS.
The external bridge requires a port on the physical external network
interface to provide instances with external network access. In essence,
this port connects the virtual and physical external networks in your
environment.
rdo or obs
Start the OVS service and configure it to start when the system boots:
# systemctl enable openvswitch.service # systemctl start openvswitch.service
ubuntu or debian
Restart the OVS service:
# service openvswitch-switch restart
Add the external bridge:
# ovs-vsctl add-br br-exAdd a port to the external bridge that connects to the physical external network interface. Replace
INTERFACE_NAMEwith the actual interface name. For example, eth2 or ens256:# ovs-vsctl add-port br-ex INTERFACE_NAMENote
Depending on your network interface driver, you may need to disable
generic receive offload (GRO)to achieve suitable throughput between your instances and the external network.To temporarily disable GRO on the external network interface while testing your environment:
# ethtool -K INTERFACE_NAME gro off
To finalize the installation
rdo
The Networking service initialization scripts expect a symbolic link
/etc/neutron/plugin.inipointing to the ML2 plug-in configuration file,/etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/ml2_conf.ini. If this symbolic link does not exist, create it using the following command:# ln -s /etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/ml2_conf.ini /etc/neutron/plugin.iniDue to a packaging bug, the Open vSwitch agent initialization script explicitly looks for the Open vSwitch plug-in configuration file rather than a symbolic link
/etc/neutron/plugin.inipointing to the ML2 plug-in configuration file. Run the following commands to resolve this issue:# cp /usr/lib/systemd/system/neutron-openvswitch-agent.service \ /usr/lib/systemd/system/neutron-openvswitch-agent.service.orig # sed -i 's,plugins/openvswitch/ovs_neutron_plugin.ini,plugin.ini,g' \ /usr/lib/systemd/system/neutron-openvswitch-agent.serviceStart the Networking services and configure them to start when the system boots:
# systemctl enable neutron-openvswitch-agent.service neutron-l3-agent.service \ neutron-dhcp-agent.service neutron-metadata-agent.service \ neutron-ovs-cleanup.service # systemctl start neutron-openvswitch-agent.service neutron-l3-agent.service \ neutron-dhcp-agent.service neutron-metadata-agent.serviceNote
Do not explicitly start the neutron-ovs-cleanup service.
obs
The Networking service initialization scripts expect the variable
NEUTRON_PLUGIN_CONFin the/etc/sysconfig/neutronfile to reference the ML2 plug-in configuration file. Edit the/etc/sysconfig/neutronfile and add the following:NEUTRON_PLUGIN_CONF="/etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/ml2_conf.ini"Start the Networking services and configure them to start when the system boots:
# systemctl enable openstack-neutron-openvswitch-agent.service openstack-neutron-l3-agent.service \ openstack-neutron-dhcp-agent.service openstack-neutron-metadata-agent.service \ openstack-neutron-ovs-cleanup.service # systemctl start openstack-neutron-openvswitch-agent.service openstack-neutron-l3-agent.service \ openstack-neutron-dhcp-agent.service openstack-neutron-metadata-agent.serviceNote
Do not explicitly start the neutron-ovs-cleanup service.
ubuntu or debian
Restart the Networking services:
# service neutron-plugin-openvswitch-agent restart # service neutron-l3-agent restart # service neutron-dhcp-agent restart # service neutron-metadata-agent restartNote
Perform these commands on the controller node.
Verify operation
Source the
admincredentials to gain access to admin-only CLI commands:$ source admin-openrc.shList agents to verify successful launch of the neutron agents:
$ neutron agent-list +-------+--------------------+---------+-------+----------------+---------------------------+ | id | agent_type | host | alive | admin_state_up | binary | +-------+--------------------+---------+-------+----------------+---------------------------+ | 302...| Metadata agent | network | :-) | True | neutron-metadata-agent | | 4bd...| Open vSwitch agent | network | :-) | True | neutron-openvswitch-agent | | 756...| L3 agent | network | :-) | True | neutron-l3-agent | | 9c4...| DHCP agent | network | :-) | True | neutron-dhcp-agent | +-------+--------------------+---------+-------+----------------+---------------------------+