Change-Id: I694301758f7f85290d4c9f9b01fbd1924b02b476 Implements: blueprint image-guide-rst
7.8 KiB
Example: Ubuntu image
This example installs a Ubuntu 14.04 (Trusty Tahr) image. To create an image for a different version of Ubuntu, follow these steps with the noted differences.
Download an Ubuntu install ISO
Because the goal is to make the smallest possible base image, this example uses the network installation ISO. The Ubuntu 64-bit 14.04 network installer ISO is at http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dists/trusty/main/installer-amd64/current/images/netboot/mini.iso.
Start the install process
Start the installation process by using either virt-manager or virt-install as described
in the previous section. If you use virt-install, do not forget to connect your VNC
client to the virtual machine.
Assume that the name of your virtual machine image is
ubuntu-14.04, which you need to know when you use virsh commands to
manipulate the state of the image.
If you are using virt-manager, the commands should look something
like this:
# qemu-img create -f qcow2 /tmp/trusty.qcow2 10G
# virt-install --virt-type kvm --name trusty --ram 1024 \
--cdrom=/data/isos/trusty-64-mini.iso \
--disk /tmp/trusty.qcow2,format=qcow2 \
--network network=default \
--graphics vnc,listen=0.0.0.0 --noautoconsole \
--os-type=linux --os-variant=ubuntutrustyStep through the install
At the initial Installer boot menu, choose the Install option. Step
through the install prompts, the defaults should be fine.

Hostname
The installer may ask you to choose a host name. The default
(ubuntu) is fine. We will install the cloud-init package
later, which will set the host name on boot when a new instance is
provisioned using this image.
Select a mirror
The default mirror proposed by the installer should be fine.
Step through the install
Step through the install, using the default options. When prompted
for a user name, the default (ubuntu) is fine.
Partition the disks
There are different options for partitioning the disks. The default
installation will use LVM partitions, and will create three partitions
(/boot, /, swap), and this will work fine.
Alternatively, you may wish to create a single ext4 partition, mounted
to "/", should also work fine.
If unsure, we recommend you use the installer's default partition scheme, since there is no clear advantage to one scheme or another.
Automatic updates
The Ubuntu installer will ask how you want to manage upgrades on your system. This option depends on your specific use case. If your virtual machine instances will be connected to the Internet, we recommend "Install security updates automatically".
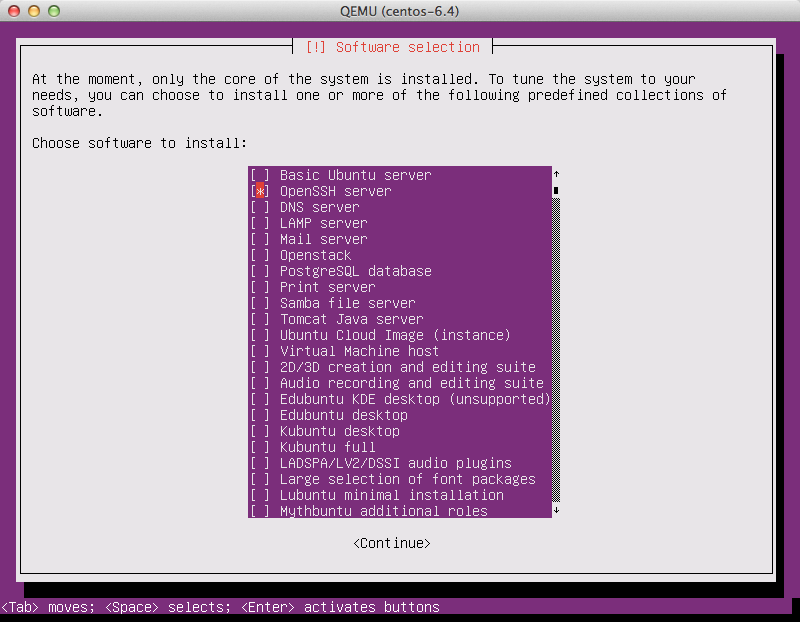
Software selection: OpenSSH server
Choose OpenSSH server so that you will be able to SSH
into the virtual machine when it launches inside of an OpenStack
cloud.
Install GRUB boot loader
Select "Yes" when asked about installing the GRUB boot loader to the master boot record.
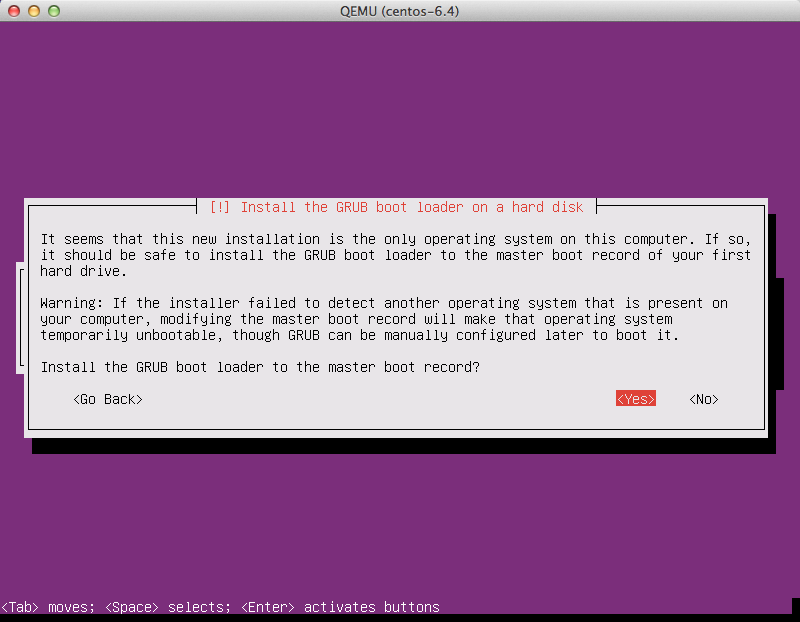
For more information on configuring Grub, see the section called
"write-to-console".
Detach the CD-ROM and reboot
Select the defaults for all of the remaining options. When the installation is complete, you will be prompted to remove the CD-ROM.
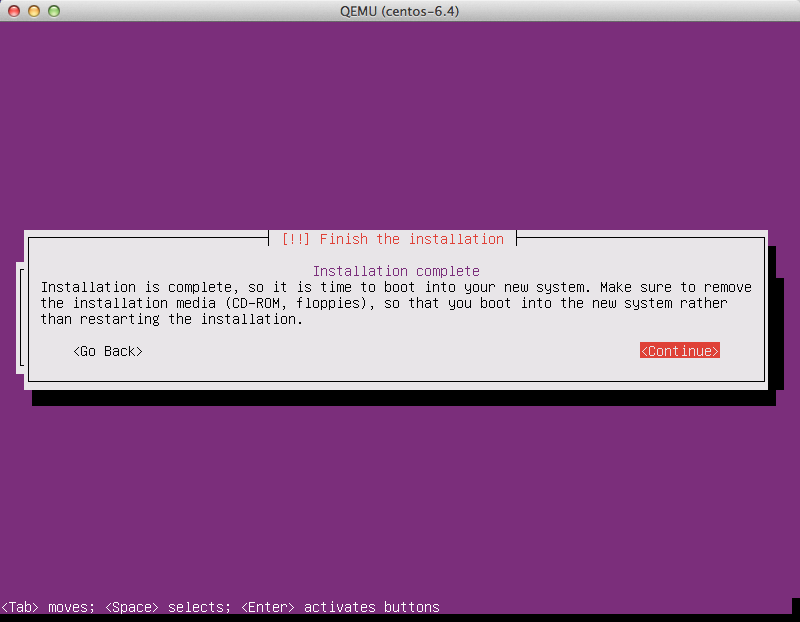
Note
There is a known bug in Ubuntu 14.04; when you select
Continue, the virtual machine will shut down, even though
it says it will reboot.
To eject a disk using virsh, libvirt requires that you attach an empty
disk at the same target that the CDROM was previously attached, which
should be hdc. You can confirm the appropriate target using
the virsh dumpxml vm-image command.
# virsh dumpxml trusty
<domain type='kvm'>
<name>trusty</name>
...
<disk type='block' device='cdrom'>
<driver name='qemu' type='raw'/>
<target dev='hdc' bus='ide'/>
<readonly/>
<address type='drive' controller='0' bus='1' target='0' unit='0'/>
</disk>
...
</domain>Run the following commands in the host as root to start up the machine again as paused, eject the disk and resume. If you are using virt-manager, you may use the GUI instead.
# virsh start trusty --paused
# virsh attach-disk --type cdrom --mode readonly trusty "" hdc
# virsh resume trustyNote
In the previous example, you paused the instance, ejected the disk,
and unpaused the instance. In theory, you could have ejected the disk at
the Installation complete screen. However, our
testing indicates that the Ubuntu installer locks the drive so that it
cannot be ejected at that point.
Log in to newly created image
When you boot for the first time after install, it may ask you about
authentication tools, you can just choose Exit. Then, log
in as root using the root password you specified.
Install cloud-init
The cloud-init
script starts on instance boot and will search for a metadata provider
to fetch a public key from. The public key will be placed in the default
user account for the image.
Install the cloud-init package:
# apt-get install cloud-initWhen building Ubuntu images cloud-init must be explicitly configured for the
metadata source in use. The OpenStack metadata server emulates the EC2
metadata service used by images in Amazon EC2.
To set the metadata source to be used by the image run the dpkg-reconfigure command
against the cloud-init package. When prompted select the
EC2 data source:
# dpkg-reconfigure cloud-initThe account varies by distribution. On Ubuntu-based virtual machines, the account is called "ubuntu". On Fedora-based virtual machines, the account is called "ec2-user".
You can change the name of the account used by cloud-init by editing
the /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg file and adding a line with a
different user. For example, to configure cloud-init to put the key in
an account named admin, edit the config file so it has the
line:
user: adminShut down the instance
From inside the instance, as root:
# /sbin/shutdown -h nowClean up (remove MAC address details)
The operating system records the MAC address of the virtual Ethernet
card in locations such as
/etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules during the
installation process. However, each time the image boots up, the virtual
Ethernet card will have a different MAC address, so this information
must be deleted from the configuration file.
There is a utility called virt-sysprep, that performs various cleanup tasks
such as removing the MAC address references. It will clean up a virtual
machine image in place:
# virt-sysprep -d trustyUndefine the libvirt domain
Now that the image is ready to be uploaded to the Image service, you
no longer need to have this virtual machine image managed by libvirt.
Use the virsh undefine vm-image command to inform
libvirt:
# virsh undefine trustyImage is complete
The underlying image file that you created with qemu-img create, such as
/tmp/trusty.qcow2, is now ready for uploading to the Image
service.